Emerging from the lush landscapes and vibrant ecosystems of the African continent, African lovebirds have become cherished members of households worldwide.
These delightful creatures range from the playful Fischer’s lovebird, adorned in hues of emerald green, to the charming peach-faced lovebird, whose cheerful disposition and striking yellow and gray plumage are hard to resist.

Introduction to African Lovebirds
African lovebirds are small, colorful parrots native to Africa. They are members of the parrot family, Psittacidae, and belong to the genus Agapornis. These endearing birds are known for their affectionate nature, playful antics, and vibrant plumage.
African lovebirds are among the most popular pet parrots worldwide, due to their gentle temperament, social nature, and intelligence. They are relatively easy to care for and can learn to mimic sounds and perform simple tricks.
Unveiling the Species Diversity of African Lovebirds
African sunbirds, a vibrant group of nectarivorous birds, captivate with their dazzling plumage and captivating courtship displays. Their feathers, often adorned with iridescent hues that shimmer under the sunlight, serve as a testament to their intricate evolutionary adaptations and their crucial role in communication and mate selection.
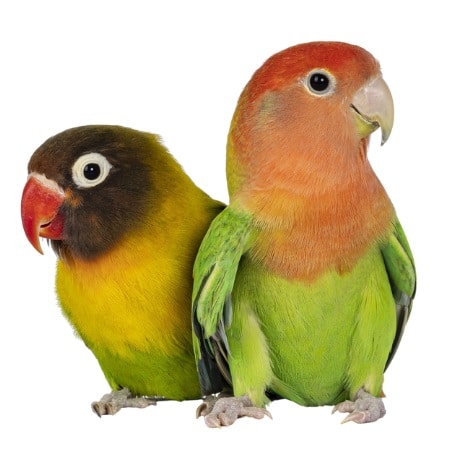

General Appearance:
African sunbirds are small to medium-sized birds, ranging in size from around 4 inches to 7 inches in length. They are characterized by their slender bodies, long, slender beaks, and diverse plumage colors. Some species boast striking green, yellow, or red plumage, while others exhibit more muted tones of brown, gray, or olive.
- Bill: African lovebirds have short, strong, conical bills that are adapted for cracking seeds.
- Tail: African lovebirds have long, tapering tails that are often colored differently from the rest of the body.
- Legs: African lovebirds have strong, sturdy legs that enable them to climb and perch with ease.
Iridescent Hues and Structural Pigmentation:
The dazzling colors of African sunbirds are not achieved through pigments found in their feathers but rather through structural features that bend and reflect light in a way that produces a range of iridescent hues. These structural pigments, known as nanoscale reflectors, create a shimmering effect that is particularly noticeable in sunlight.
Communicating Intents
African sunbirds employ their vibrant plumage to convey a variety of intentions, both within their social groups and during courtship rituals. These visual cues serve as powerful nonverbal communication tools, enabling them to express their emotions, establish dominance hierarchies, and attract mates.
- Expressing Emotions: The intensity of coloration and the specific color patterns can indicate the emotional state of an African sunbird.
- Establishing Dominance: Plumage patterns and the way they are displayed can play a crucial role in establishing dominance hierarchies within sunbird flocks. Dominant males often exhibit more vibrant and complex plumage.
- Attracting Mates: During courtship rituals, African sunbirds engage in elaborate displays that incorporate their striking plumage. Males will often perch in prominent locations, fanning their feathers and performing intricate movements to attract the attention of females.
Why Are African Lovebirds Popular Pet Birds?
African lovebirds are popular pet birds for several reasons:
- Affectionate Nature: African lovebirds form strong bonds with their owners and enjoy being cuddled and petted.
- Playful Antics: African lovebirds are naturally playful and enjoy exploring their surroundings and interacting with toys.
- Intelligence: African lovebirds are intelligent birds that can learn to mimic sounds and perform simple tricks.
- Vocal Abilities: African lovebirds are relatively vocal birds and can be trained to speak.
- Social Nature: African lovebirds are social birds that thrive on companionship and interaction with their owners or other birds.
- Easy to Care for: African lovebirds are relatively easy to care for and require a spacious cage, a balanced diet, and regular interaction.
In addition to these desirable traits, African lovebirds are also relatively affordable compared to other parrot species. As a result, they have become a popular choice for pet enthusiasts of all ages.

A Flock of Names: The 6 Species Unveiled
1. Fischer’s Lovebird
- Latin Name: Agapornis fischeri
- Size (Inches): 5-6
- Distinctive Features: Male: Fischer’s Lovebirds are small parrots with predominantly green plumage. They have a bright orange face and forehead, and the crown of the head is often a deeper shade of orange. The throat, chest, and abdomen are yellow, and the back and wings may have a blue tinge. The beak is red, and the eyes are surrounded by a white eye-ring
- Unique Aspects: Relatively easy to care for and train and are known for their energetic and social nature. They form strong pair bonds and are often seen in small flocks.
- Found in: Native to a limited region in east-central Africa, specifically in Tanzania. In the wild, they inhabit a variety of environments, including savannas and scrublands.
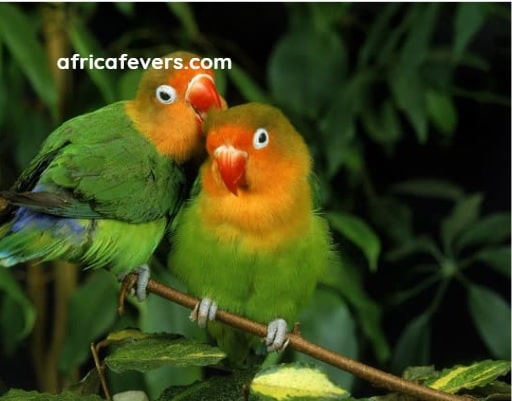

2. Peach-faced Lovebird
- Latin Name: Agapornis roseicollis, also commonly known as the Rosy-faced Lovebird
- Size (Inches): 5-6
- Distinctive Features: Peach-faced Lovebirds have predominantly green plumage. They are named for the peach-colored face and throat, which contrast with the bright blue feathers around the eyes. The forehead and crown are a deeper shade of blue. The beak is horn-colored, and the eyes are surrounded by a white eye-ring. The abdomen and chest may have a pinkish hue.
- Unique Aspects: Popular pet bird due to its affectionate nature and playful behavior. They are social birds that form strong pair bonds. In the wild, they often gather in flocks and can be found in various habitats, including savannas and scrublands.
- Location: South Africa, Namibia, and Botswana, Angola
3. Red-headed Lovebird
- Latin Name: Agapornis Pullarius also known as the Black-cheeked Lovebird.
- Size (Inches): 6-7
- Distinctive Features: The Red-headed Lovebird has predominantly green plumage. It is characterized by a red or orange head and face, with some darker feathers on the cheeks. The upper chest is often yellow, and the beak is horn-colored
- Unique Aspects: Relatively large and bold personality
- Found in Angola, Cameroon, Nigeria, and the Ivory Coast.
4. Black-masked Lovebird
- Latin Name: Agapornis personatus, also known as the Yellow-collared Lovebird,
- Size (Inches): 5-6
- Distinctive Features: The Black-masked Lovebird has predominantly green plumage. It is characterized by a black or dark brown face mask that extends across the eyes and cheeks, giving it its name. The upper chest is typically yellow, and the beak is red-colored. They have a short, square-shaped tail.
- Unique Aspects: Vocal and active bird, enjoys playing with toys. Black-masked Lovebirds are social birds and often form small flocks.
- Native to Tanzania.
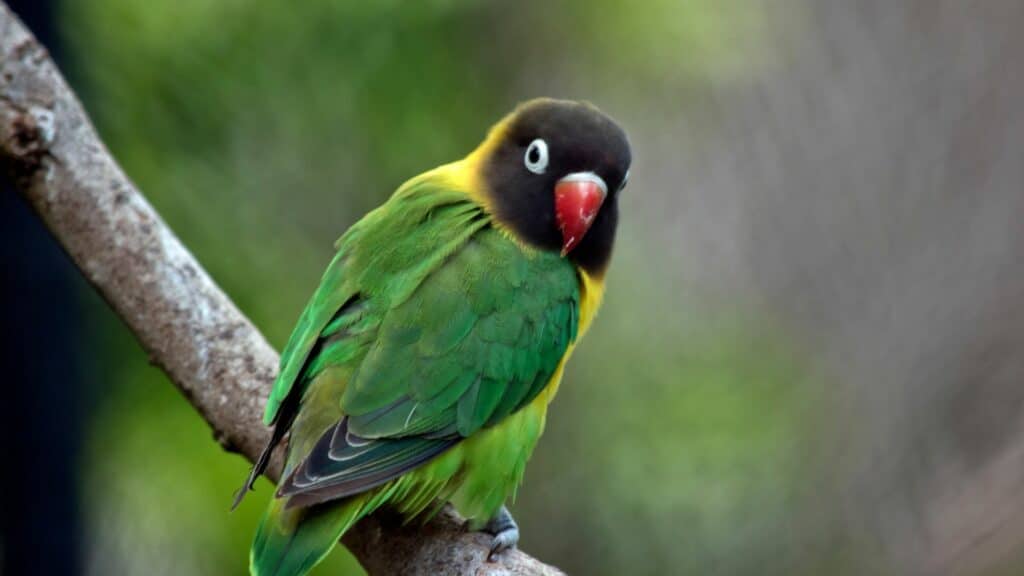

5. Grey-headed Lovebird or Madagascar Lovebird
- Latin Name: Agapornis canus
- Size (Inches): 5-6
- Distinctive Features: a small parrot with predominantly green plumage. It has a greyish head, hence the alternative name “Grey-headed Lovebird.” The beak is typically reddish-orange, and the eyes are surrounded by a white eye ring.
- Unique Aspects: Relatively quiet and calm bird, enjoys foraging for food
- Location: Madagascar: amongst the endemic birds of Madagascar.
6. Lilian’s Lovebird
- Latin Name: Agapornis lilianae
- Size (Inches): 5-6
- Distinctive Features: Lilian’s Lovebird is a small parrot with predominantly green plumage. It has a distinctively orange-red head, neck, and upper chest. The beak is typically horn-colored, and the eyes are surrounded by a white eye-ring. The tail is short and squared.
- Unique Aspects: Rare species, known for its gentle and affectionate nature
- Location : South Western Africa
- Lilian’s Lovebird is classified as “Near Threatened” on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List.
Romance is in the Air: Mating Behaviors of Lovebirds
African lovebirds are known for their vibrant plumage and charming personalities, but they’re also masters of the art of courtship. When a lovebird is smitten with another, they engage in a series of elaborate rituals to attract their attention.
Courtship Rituals
Lovebirds begin their courtship with a series of vocalizations, including soft chirps, whistles, and even mimics of human sounds. They may also perform synchronized dances, where they sway and bob their heads in unison.
Once a pair has formed, they become incredibly devoted to each other. They often spend hours grooming each other, and they may even sleep in the same nest. Lovebirds are typically monogamous for life, and they will mate for several years before they start producing offspring.
The bond between lovebirds is so strong that they will often go to great lengths to stay together. If one partner dies, the other may grieve for months, and they may refuse to mate with another bird.
Nesting
When a couple is ready to raise a family, they will build a nest together. Lovebirds are cavity nesters, and they will often use hollow trees or old termite mounds. Once the nest is complete, the female will lay a clutch of 3-8 eggs.
Lovebirds are social birds, and they enjoy interacting with each other. They will often play together, and they may even engage in mock battles. These interactions help to strengthen the pair’s bond and prepare them for raising their young.
Where to Find Lovebirds: their habitat and conservation status.
African lovebirds inhabit diverse habitats, each species exhibiting unique preferences that influence their distribution.
Please be aware that conservation statuses are subject to change, and it’s advisable to check the latest information from reputable sources or conservation organizations for the most up-to-date assessments.
| Lovebird Species | Habitat | Conservation Status |
|---|---|---|
| Fischer’s Lovebird | Woodlands and savannas in Tanzania | Least Concern |
| Peach-faced Lovebird | Arid regions, including savannas and scrublands in Southwestern Africa | Least Concern |
| Red-headed Lovebird | Wooded areas, savannas, and forests in Central and West Africa | Least Concern |
| Black-masked Lovebird | Savannas, woodlands, and scrublands in Northeastern Tanzania | Least Concern |
| Grey-headed Lovebird (Madagascar Lovebird) | Various habitats in Madagascar | Near Threatened |
Habitat loss poses a significant threat to these captivating birds. As forests are cleared for agriculture, timber, and urbanization, lovebirds lose their vital nesting sites and foraging grounds, leading to population declines and even extinction.
Conservation efforts aimed at protecting existing forests, creating new ones, and reducing the demand for illegal wildlife trade are crucial to safeguarding these colorful creatures.

African Lovebirds’ Menu: What’s for Dinner?
African lovebirds are omnivorous birds, meaning that they eat a variety of foods. In the wild, their diet consists of seeds, fruits, berries, nectar, and insects. They will also occasionally eat small pebbles and pieces of wood to aid in digestion.
Seeds
Seeds are a staple of the lovebird diet. They provide lovebirds with essential nutrients such as protein, fat, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Some of the most common seeds that lovebirds eat include millet, sunflower seeds, and safflower seeds.
Fruits and Berries
Lovebirds also enjoy eating fruits and berries. These foods are high in antioxidants, which can help to protect their health from free radicals. Some of the fruits and berries that lovebirds eat include apples, bananas, grapes, and berries.
Nectar
Lovebirds are attracted to the sweet nectar of flowers. They will often suck the nectar from flowers, and they may also eat the pollen. Nectar provides lovebirds with energy and fluids.
Insects
In the wild, lovebirds will eat insects to supplement their diet. Insects are a good source of protein and other nutrients. Some of the insects that lovebirds eat include crickets, mealworms, and caterpillars.
Pebbles and Wood
Lovebirds will occasionally eat pebbles and pieces of wood. This helps to grind down their food and aid in digestion.
Feeding Schedule
Lovebirds should be fed a variety of foods throughout the day. They should have access to fresh water at all times. Lovebirds should also be given a variety of toys to keep them entertained.
Here is a sample feeding schedule for lovebirds:
- Breakfast: A mixture of seeds, fruits, and vegetables
- Midday: A small amount of insects
- Evening: A small amount of pellets
Tips for Feeding African Lovebirds
- Always wash fruits and vegetables before feeding them to your lovebird.
- Remove any uneaten food from the cage after a few hours.
- Store seeds, fruits, and vegetables in the refrigerator to keep them fresh.
- Regularly check your lovebird’s food and water bowls for any signs of mold or contamination.
By following these tips, you can help to ensure that your African lovebird is getting the nutrients that they need to stay healthy and happy.
Creating a Love Nest: Caring for Lovebirds in Captivity
Lovebirds are social and intelligent birds that require a stimulating and enriching environment to thrive. Here are some guidelines for creating an ideal home for your lovebird:
- Cage: The cage should be large enough for your lovebird to spread its wings and move around comfortably. A cage size of 24″ x 18″ x 18″ is a good starting point for a single lovebird. The cage should have plenty of perches of different sizes and textures, as well as toys to keep your lovebird entertained.
- Food and Water: Provide your lovebird with a variety of food options, including a seed mix, fresh fruits and vegetables, and a small amount of insects. Place food and water bowls at the bottom of the cage. Make sure to clean the food and water bowls regularly.
- Heating and Lighting: Lovebirds are sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Ensure the room temperature stays between 65 and 80 degrees Fahrenheit. Provide your lovebird with a heat source if needed, such as a heat lamp or a heat mat. Lovebirds also require 12 hours of darkness each night for proper sleep.
- Social Interaction: Lovebirds are social birds and need plenty of interaction with their owners. Spend time with your lovebird each day, talking to it, playing with it, and training it. If you can, provide your lovebird with a companion bird.
- Mental Stimulation: Lovebirds are intelligent birds and need plenty of mental stimulation to keep them from becoming bored. Provide your lovebird with a variety of toys, including foraging toys, puzzle toys, and shredding toys. You can also create your own toys using household items such as toilet paper rolls, paper bags, and empty cardboard boxes.
The Importance of Social Interaction and Mental Stimulation
Social interaction and mental stimulation are essential for the well-being of lovebirds. Without enough social interaction, lovebirds can become lonely, depressed, and even aggressive. Without enough mental stimulation, lovebirds can become bored, which can lead to destructive behaviors such as feather plucking.
Here are some ways to provide your lovebird with the social interaction and mental stimulation it needs:
- Spend time with your lovebird each day: Talk to it, play with it, and train it.
- Provide your lovebird with a companion bird: This will give your lovebird someone to interact with and play with.
- Provide your lovebird with a variety of toys: This will help to keep your lovebird entertained and mentally stimulated.
- Create a stimulating environment for your lovebird: This could include hanging bird swings, providing ladders, or putting up mirrors.
Recommendations for Healthcare
Lovebirds are generally healthy birds, but they can be susceptible to certain health problems. Here are some recommendations for keeping your lovebird healthy:
- Regularly check your lovebird’s feathers, beak, and feet for any signs of injury or illness.
- Take your lovebird to the veterinarian for regular checkups.
- Keep your lovebird’s cage clean and free of debris.
- Provide your lovebird with a balanced diet.
- Avoid exposing your lovebird to secondhand smoke and other harmful toxins.
Breeding Lovebirds in Captivity
Breeding lovebirds in captivity can be a rewarding experience, but it is important to do your research and make sure you are prepared for the challenges and responsibilities involved. Here are some things to consider before breeding lovebirds:
- Provide your lovebirds with a spacious cage with plenty of nesting material.
- Make sure your lovebirds are healthy and of breeding age.
- Incubate the eggs and raise the chicks yourself, or find a reputable breeder to do it for you.
- Be prepared for the chicks to need a lot of attention and care.
If you are considering breeding lovebirds, it is important to talk to a veterinarian or avian expert to get more information and advice.
FAQs on the African Lovebirds
As always at the end of an article, I always answer some FAQs for you on the topic, so here we go!
Are African Lovebirds good pets?
I would say that the African Grey is a bit easier then keeping an African Lovebird as a pet, but it can be done. Preferably get an African lovebird as a pair, because they are very affectionate.
Are African Lovebirds actually parrots?
Yes, they belong to a small group of parrots.
Can you tame African lovebirds?
You can tame an African Lovebird, but as with any pet, it can depend on the situation. Taming it from a young age or an adopted bird, for example, can make a big difference.
Do they mate for life?
Yes, they are mating for life and will suffer if one bird passes away.
Related articles:
My Final Conclusion.
I hope that you found this article on African Lovebirds interesting and informational, but if you have any questions or suggestions, please feel free to leave them down below in the comment section.
You can also join me on my social media channels below for more pictures, videos, and stories on my Africa travels, welcome!
I wish you happy travels!
Kind regards,
Lizzy
I now have a YouTube channel as well!
YouTube
Hello Africa travellers!
Who am I? Well, the least you can say is that I am quite crazy about Africa, its nature, its climate, its culture, and more.
As a young woman in my twenties, I had already traveled to several African countries by traveling along in an overlander on my own and mostly camping ( or glamping ) and just fell in love with the diversity of it all.
So much, so that at the age of 26, I went back to university to study biology, which, unfortunately, I couldn’t finish because of health reasons (yes, I got sick from a tropical disease, oh cynicism). But this did not stop my dream of traveling back to Africa several times, and I still do.
My dream was back then to leave Europe and go study animal behavior, especially the elephants (sure, that’s every girl’s dream haha), but I am also very much intrigued by hyenas and other “ugly African animals“.
So, I “kind of” have a little bit of a scientific approach to my articles, when I write about African birds, for example. And most of all: the passion.
But life goes on, you move from one side of the country to the other, you get sick again and top it off with lower back problems, and before you know it, you are over 50 hahaha!
Now, I still travel to Africa, but take it a bit “easier” than the good old camping days, and stay in comfortable, yet affordable accommodations, together with my husband Wouter.
These are some of the countries I have traveled to: Kenya, Tanzania, Zanzibar, Malawi, Zambia, Zimbabwe, South Africa, Namibia, Botswana, Tunisia, and a little bit of Lesotho LOL .
While clearly not being African territory, but Spanish, I also visited Gran Canaria and Tenerife, and location-wise, I consider them “African”, because of their climate and nature, sue me :-p
The last trip I took was to South Africa in the year 2023, and it sure got the fevers for Africa back! From the Barberton mountains to the Drakensberg and the Southcoast, one month wasn’t enough at all to see the whole country, so we’ll be back! At ease and with a little bit more luxury than in my younger days haha!
I wish you happy travels!
Kind regards
Lizzy










Wow, your blog post on African Lovebirds is incredibly captivating! I enjoyed learning about the diverse species and their unique characteristics, especially the stunning iridescent hues achieved through structural pigmentation. The detailed descriptions of each species, their habitats, and conservation statuses provide a well-rounded perspective. Keep up the fantastic work! 🦜✨
Hello Hanna!
Thank you very much for your positive comment, I do my best 😉
Lizzy
Hey Lizzy,
What a lovely article. You’ve provided so much information and details. Thank you.
These birds look beautiful and how you have described them and their characteristics, you can tell why they are called love birds. Really appreciated the videos as this helps to see the birds in action.
During your travels to Africa, did you encounter any of these in the wild?
Thanks again for a great article.
Cherie :o)
Hello Cherie!
You are very welcome, aren’t they adorable? 🙂
About your questions: unfortunately, I haven’t spotted these birds myself yet, but I would surely like to!
They are called Lovebirds, because pairs of Lovebirds are very much attached to each other and they bond for life, talk about romance! 🙂
Thanks for your comment!
Lizzy